Mybatis框架简介
属于主流的持久层[和db交互的层,负责和db打交道]框架,不负责业务操作.只会涉及到sql语句的编写.
属于ORM[对象关系映射 - 表和实体类息息相关的关系]框架,ORM是一个思想.ORM框架就是这个思想的”实现者”
Mybatis是属于半自动的ORM框架 - MyBatis 免除了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的工作.
复杂的查询那么仍然是需要手动进行映射的[列-属性]
Mybatis底层是基于jdbc代码的.
mybatis前身叫ibatis
Mybatis环境的搭建
使用框架之前,都是需要经过繁琐的配置的.除了SpringBoot[简化了配置]
最新版本 - 3.5.7 - https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/releases
导入jar
项目的根目录下新建一个lib目录 - 用来存放第三方jar
1-1. mysql-connector-java-8.0.25.jar - mysql的驱动jar包
1-2. mybatis-3.5.7.jar - mybatis的jar包
选中jar - 右击 - Add As Library … - 把这俩个jar添加到类路径中[classpath]
配置文件
框架的配置文件要么是properties文件[支持,优先级是最高的],本次课程中推荐使用的配置文件是xml文件[结构比较清晰]
等待后面学习SpringBoot - 推荐使用的配置文件是yml文件[yarn语法]
- mybatis的主配置文件
- mapper的映射文件 - 存储项目中的所有的sql语句.sql语句和应用程序进行了分离,方便sql语句的维护.
mybatis的主配置文件
mybatis的运行时环境,mybatis框架能够被使用的前提是肯定会去读取这个配置文件.配置了该框架运行所有应该具备的信息.
推荐 - 放在src的根目录下mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!-- 配置环境的选择 - 开发环境下的配置 环境 - 开发环境,测试环境,产品上线[部署]环境 通过default的属性值来指定哪种环境会生效 --> <environments default="dev"> <environment id="dev"> <!-- mybatis的事务就是采用jdbc事务[由底层的数据库驱动决定了]--> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <!--配置数据源的 - POOLED - 相当于连接池 - 使用mybatis自带的--> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/j03s?useSSL=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="root"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> </configuration>
核心API
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
仅仅只会使用到一次.
SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream in);
功能:读取xml的字节输入流来构建一个重量级的对象SqlSessionFactory - 相当于jdbc数据源对象[BasicDataSource].
SqlSessionFactory
重量级的对象 - 不能随意创建多个或者随意销毁 - 耗时间 - 占内存 - 单例
一旦被创建就应该在应用的运行期间一直存在,没有任何理由丢弃它或重新创建另一个实例
SqlSession openSession();//获取Session对象
SqlSession
作用:负责和db进行CRUD操作.
与db进行一次会话 - 一次连接.相当于JDBC中的Connection对象.但是比jdbc多出缓存的功能.
SqlSession=Connection[db连接] + Cache[默认的一级缓存];
SqlSession 的实例不是线程安全的,因此是不能被共享的.每个线程都应该有它自己的 SqlSession 实例.
session应该是一个局部变量
回顾java知识点当线程执行到方法的时候,就会在本地开辟一块区域 - 线程栈[独占的]
传统的开发方式
db设计 - 实体类设计 - User - Video
编写IUserDao接口,UserDaoImpl接口实现类
User user = session.selectOne("userMapper.get",username);编写映射文件 - tech/aistar/mapperxml - 目录下存储所有的映射文件user-mapper.xml
需要在mybatis-config.xml文件中配置映射文件.
<mappers> <!-- 指定映射文件的配置路径--> <mapper resource="tech/aistar/mapperxml/user-mapper.xml"></mapper> </mappers>
剖析
1. session = MybatisUtil.getSession(); 观察MybatisUtil - 读取了mybatis-config.xml文件 - user-mapper.xml2. 俩个文件都被加载到JVM内存了. user-mapper.xml里面的信息都是在内存中了. namespace="userMapper"应该是唯一的,一个namespace应该是对应唯一的映射文件. 因为项目中可能有多个映射文件.Map<String,xml映射对象> maps maps.put("userMapper",xml文件对应的映射对象);3. selectOne(namespace.sql语句id值) XMl映射对象 变量 = maps.get("userMapper");//精准的定位到它自己的xml文件.4. xml文件中会有很多个sql标签 - 每个sql标签的id应该是唯一的.精确拿到select标签5. 定位到select标签之后,利用xml的dom解析技术 - 标签体中的内容/标签属性的值 select * from t_user where username = #{username} resultType="tech.aistar.model.entity.User"6. Class<?> c = Class.forName("tech.aistar.model.entity.User"); jdbc编程步骤 pst = conn.preparedStatement(sql); T t = null; 判断参数个数 - 发送参数 rs=pst.executeQuery(); if(rs.next()){ // }
映射文件配置注意点
配置别名
在mybatis-config.xml文件中进行配置
<!-- 配置类型的别名--> <typeAliases> <!-- 一个一个配置--> <!-- <typeAlias type="tech.aistar.model.entity.User" alias="u"></typeAlias>--> <!-- 对项目中的实体类统计进行配置--> <!-- 扫包 - 实体类所在的包,默认分配一个别名,就是类型的小写--> <package name="tech.aistar.model"/> </typeAliases>
parameterType和resultType
parameterType对应的参数的类型
内置对象的对象类型或者基本类型,可以简便的使用这些类型的别名,底层进行了特殊的处理了
比如:parameterType=”java.lang.String”可以简单表示为parameterType=”string”
比如:long->long或者别名_long.
①推荐如果遇到的基本数据类型,直接写它名称本身即可int->int
②如果遇到包装类型,推荐写它对应的基本类型的名称[就是包装类型的别名]
③内置的对象类型,诸如String,Date,Map,List等可以写它们的别名[这些单词的小写字母]
resultType
只有select标签才需要指定resultType属性
mybatis什么时候才能够实现自动映射的效果 - 一定是查询出来的列名和实体类属性名高度保持一致
或者出来的列名是一个合法的匈牙利命名 - 实体类属性的小驼峰.
绑定失败的场景:
resultType="user" select id uid,username uname,password,birthday from t_user where username = #{username} User{id=null, username='null', password='654321', birthday=Thu Aug 26 00:00:00 CST 2021}
为什么绑定失败JdbcNBUtil.java
String colName = rsmd.getColumnName(i);
colName = changeColName(colName);//防止出现了匈牙利 -> 小驼峰Field f = c.getDeclaredField(colName);//冒出来了uid和冒出uname - > 反射找不到对应的Field或者Method
说明了id和username并没有通过反射设置值.
resultMap
应用场景一: 当查询的列值不能自动映射/绑定实体类的属性的时候,需要通过resultMap来进行一一绑定.
mybatis有些场景下还是需要手动绑定 - 半自动的ORM框架.
<!-- 手动映射--> <resultMap id="get_map" type="user"> <!-- 主键列映射--> <id column="uid" property="id"></id> <!-- 普通列映射--> <result column="uname" property="username"></result> <result column="birthday" property="birthday"></result> <result column="password" property="password"></result> </resultMap> <select id="get" parameterType="string" resultMap="get_map"> select id uid,username uname,password,birthday from t_user where username = #{username} </select>
剖析一下手动绑定的过程
type="tech.aistar.model.pojo.user" - >
Class<?> c = Class.forName(type);
T t = (T)c.newInstance();
result标签的顺序可以随机的 -> 说明底层 - rs要么根据列的序号取[从1开始],可以根据列的名称去取.
Object getObject(String columnLabel) throws SQLException;
Object uname = rs.getObject("uname");
property="username" -> 底层"setUsername"->
Method m = c.getDeclaredMethod("setUsername");
m.invoke(t,uname);//反射调用setter方法.
加入method找不到 - Field f = c.getDeclaredField("username");
f.set(t,uname);
如果property="属性值"找不到任何一个对应的method或者field -> 直接抛出
There is no setter for property named 'usernames' in 'class tech.aistar.model.entity.User'
selectOne和selectList区别
selectOne - 负责加载唯一的一条数据 - 返回的是一个单个对象
selectList - 负责加载多条数据,返回一个集合
如果在必须使用selectList,不小心使用到了selectOne.那么就会抛出异常
org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.TooManyResultsException: Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: 5
练习IVedioDao
完成crud
卡壳 - 不断抛出异常 - “思考代码-表面-背后“ - “理解规则 - 遵守规则” + 规范
idea中配置映射文件的模板
点击+
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="">
</mapper>
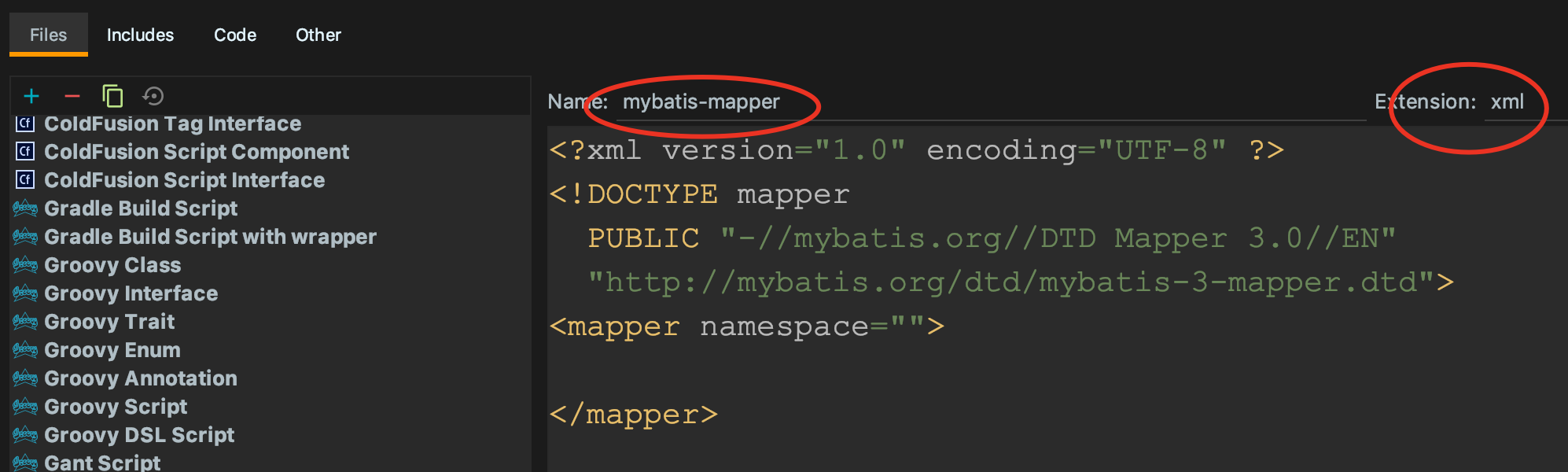
点击apply - ok
匈牙利<->小驼峰自动映射
<select id="getById" resultType="video" parameterType="int">
select * from t_video where id=#{id}
</select>
列 - video_url user_id create_date
-- 设置失败.
Video{id=20, title='国庆节2', createDate=null, price=100.0, videoUrl='null', userId=null}
第一种处理方式 - 使用resultMap手动进行映射.
第二种处理方式 - 针对db中的特殊的匈牙利的命名方式 - 在mybatis-config.xml文件中进行设置.
<!-- 开启小驼峰命名映射-->
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
占位符区别$和#
建议完善俩者区别
$ - 产生了sql注入的问题,把参数直接硬拼接到了sql中.相当于Statement
井号
#{参数} - 相当于PreparedStatement,占位符? //提前将这条语句进行预编译的. #{title} -> ? //设置参数和发送参数 select * from t_video where title = #{title}
剖析
select * from t_video where title = #{title}
select * from t_video where title = ${title}
报错的原因:控制台已经后台生成的sql显示出来了 -
select * from t_video where title = 国庆节2;
把findByTile中的字符串参数直接硬拼接到了sql语句的占位符号去了.
@Test
public void testFindByTitle(){
videoDao.findByTitle("国庆节2").forEach(e-> System.out.println(e));
}
// 非要使用${title}
select * from t_video where title = '${title}'
videoDao.findByTitle("国庆节2").forEach(e-> System.out.println(e));
select * from t_video where title = '国庆节2';//ok
//产生sql注入了
videoDao.findByTitle("国庆节3' or'1'='1").forEach(e-> System.out.println(e));
select * from t_video where title = '国庆节3' or'1'='1';
参数名
如果是简单类型 - 单个参数[String,包装类型,基本数据类型]
#{参数名}和${参数名}是任意取名称的. id=#{ttt} id=#{value} id=#{id} 本质上#{参数} 等同于 ? <select id="getById" resultType="video" parameterType="int"> select * from t_video where id=#{id} </select> 推荐使用使用的是#{value}或者#{方法的参数的名称}
如果是自定义的对象类型 - 不能瞎写
<insert id="save" parameterType="video"> insert into t_video values(#{id},#{title},#{createDate},#{price},#{videoUrl},#{userId}) </insert>
作业
评论 - crud
Mapper代理开发方式
底层使用到的技术就是动态代理 - 动态代理技术[JDK]来在程序的运行期间来生成Mapper接口的实现类.
传统的方式还是需要手动写接口的实现类的.
遵守Mapper开发方式的规范 - 一定要遵守
创建包tech.aistar.mapper - 存放mapper接口
替代之前的dao包下的dao接口
制定Mapper接口 - 接口的命名必须要规范 - 实体类名Mapper - 比如UserMapper,VideoMapper
在Mapper接口中制定方法
一定是在Mapper接口所在的包下新建Mapper接口对应的映射文件,并且映射文件的命名一定要和它对应的Mapper接口的命名高度保持一致 - 映射文件的存放位置以及映射文件的命名
每个映射文件都会指定唯一的一个namespace属性值 - 一定是这个映射文件对应的那个Mapper接口的全限定名.
select,update,insert,delete这些sql标签的id属性的值一定要和mapper接口中的方法的名称高度保持一致.
mybatis-config.xml文件中配置映射文件.
<mappers> <!-- 指定映射文件的配置路径--> <!-- <mapper resource="tech/aistar/mapperxml/user-mapper.xml"></mapper>--> <!-- <mapper resource="tech/aistar/mapperxml/video-mapper.xml"></mapper>--> <!-- 直接扫接口 - 一个一个扫--> <!-- <mapper class="tech.aistar.mapper.UserMapper"></mapper>--> <!-- <mapper class="tech.aistar.mapper.VideoMapper"></mapper>--> <!-- 直接扫所有mapper接口所在的目录即可--> <package name="tech.aistar.mapper"/> </mappers>
mapper编程步骤
//1. 获取连接 //2. 获取Mapper接口对象 //3. 接口对象调用方法 //4. commit/关闭连接
剖析Mapper动态代理底层
搞懂为什么需要遵守这些规范
//底层如何构建UserMapper的实现 //userMapper是一个代理对象 //此处仅仅是在获取Mapper UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); //为什么就可以顺利执行到那条sql //代理对象调用方法的时候,比如会走invoke - 必然会想办法找到id="findAll"的sql语句 //比如findAll方法->对应的Method实例传入invoke->String getName();//->findAll->sql语句id属性值 List<User> userList = userMapper.findAll();
第一步
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
build方法查看build方法
//inputStream - mybatis-config.xml的字节输入流 public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) { return this.build((InputStream)inputStream, (String)null, (Properties)null); }继续查看this.build方法
//读取mybatis-config.xml 返回一个SqlSessionFactory重量级的对象 public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) { SqlSessionFactory var5; try { //功能 - 就是xml解析 XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties); //mybatis-config.xml文件中的内容解析出来 - Java内存可以拿到xml文件中的配置信息了 //拿到配置信息之后进行下一个动作 var5 = this.build(parser.parse()); } catch (Exception var14) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", var14); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException var13) { } } return var5; }this.build(parser.parse());
参数parser.parse()从mybatis-config.xml文件中解析出来的每个数据把xml配置文件中的解析出来的数据封装到了Configuration对象
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) { return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config); }大概观察一下Configuration类 { protected Environment environment; protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase; } <setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/> xml解析-mapUnderscoreToCamelCase - true "mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" - Field - 反射设置对象字段中的mapUnderscoreToCamelCase值为true
以上4步 - mybatis-config.xml -> Configuration对象
继续观察Configuration类内部
//Mapper注册机 - 想象成Mapper的容器 - 工厂 protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry; public Configuration(){ //底层肯定是使用到了Configuration对象.映射文件的信息也是配置在了mybatis-config.xml文件中的. this.mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this); }定位到MapperRegistry
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap(); //返回一个单个Mapper接口的动态代理对象 public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory)this.knownMappers.get(type); if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); } else { try { //动态代理 return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception var5) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + var5, var5); } } }回到Configuration类中
//需要把所有的配置的mapper接口全部用动态代理技术构建好之后放入到 knownMappers //观察的方法 public void addMappers(String packageName) { this.mapperRegistry.addMappers(packageName); } public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) { this.mapperRegistry.addMapper(type); }分别代表mybatis-config.xml文件中关于映射的配置的俩种方式 <mappers> <!-- <mapper class="tech.aistar.mapper.UserMapper"></mapper>--> <!-- <mapper class="tech.aistar.mapper.VideoMapper"></mapper>--> <!-- 直接扫所有mapper接口所在的目录即可--> <package name="tech.aistar.mapper"/> </mappers>
扫包public void addMappers(String packageName) { this.addMappers(packageName, Object.class); } 继续观察this.addMappers public void addMappers(String packageName, Class<?> superType) { ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil(); resolverUtil.find(new IsA(superType), packageName); Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses(); Iterator var5 = mapperSet.iterator(); while(var5.hasNext()) { Class<?> mapperClass = (Class)var5.next(); //把配置的包下的所有的接口的全限定名 -> 接口的Class实例 this.addMapper(mapperClass); } }
继续this.addMapper(mapperClass)public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) { if (type.isInterface()) { if (this.hasMapper(type)) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry."); } boolean loadCompleted = false; try { //重点的需要在第八步分析的代码 this.knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory(type)); MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(this.config, type); parser.parse(); loadCompleted = true; } finally { if (!loadCompleted) { this.knownMappers.remove(type); } } } }
5~7 - mybatis-config.xml中的关于映射文件的配置 - 底层是如何处理的 - 存储所有的Mapper接口
Map<Class, MapperProxyFactory> knownMappers = new HashMap();
观察this.knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory(type));
定位到了MapperProxyFactory类中了 - 负责构建每个Mapper接口的代理对象 - MapperProxy
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // package org.apache.ibatis.binding; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; import org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy.MapperMethodInvoker; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; public class MapperProxyFactory<T> { //每个具体的Mapper接口的class类型 private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap(); public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) { this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; } public Class<T> getMapperInterface() { return this.mapperInterface; } public Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> getMethodCache() { return this.methodCache; } protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{this.mapperInterface}, mapperProxy); } public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession, this.mapperInterface, this.methodCache); return this.newInstance(mapperProxy); } }
核心 - 找了MapperProxy动态代理对象
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { private final SqlSession sqlSession; private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperProxy.MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache; public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperProxy.MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache) { this.sqlSession = sqlSession; this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; this.methodCache = methodCache; } public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { return Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass()) ? method.invoke(this, args) : this.cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, this.sqlSession); } catch (Throwable var5) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var5); } } }invoke方法 - 什么时候会被调用的??? - 当使用代理对象去调用原始对象中的方法的时候.
List
userList = userMapper.findAll();//invoke 分析invoke中的this.cachedInvoker(method)
private MapperProxy.MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable { try { return (MapperProxy.MapperMethodInvoker)MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(this.methodCache, method, (m) -> { if (m.isDefault()) { try { return privateLookupInMethod == null ? new MapperProxy.DefaultMethodInvoker(this.getMethodHandleJava8(method)) : new MapperProxy.DefaultMethodInvoker(this.getMethodHandleJava9(method)); } catch (InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException | NoSuchMethodException | IllegalAccessException var4) { throw new RuntimeException(var4); } } else { //有效代码 - new MapperMethod(this.mapperInterface, method, this.sqlSession.getConfiguration()) return new MapperProxy.PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(this.mapperInterface, method, this.sqlSession.getConfiguration())); } }); } catch (RuntimeException var4) { Throwable cause = var4.getCause(); throw (Throwable)(cause == null ? var4 : cause); } }new MapperMethod(this.mapperInterface, method, this.sqlSession.getConfiguration())
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) { this.command = new MapperMethod.SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method); this.method = new MapperMethod.MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method); } public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Object result; Object param; switch(this.command.getType()) { case INSERT: param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(this.command.getName(), param)); break; case UPDATE: param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(this.command.getName(), param)); break; case DELETE: param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(this.command.getName(), param)); break; case SELECT: if (this.method.returnsVoid() && this.method.hasResultHandler()) { this.executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args); result = null; } else if (this.method.returnsMany()) { result = this.executeForMany(sqlSession, args); } else if (this.method.returnsMap()) { result = this.executeForMap(sqlSession, args); } else if (this.method.returnsCursor()) { result = this.executeForCursor(sqlSession, args); } else { param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param); if (this.method.returnsOptional() && (result == null || !this.method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) { result = Optional.ofNullable(result); } } break; case FLUSH: result = sqlSession.flushStatements(); break; default: throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + this.command.getName()); } if (result == null && this.method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !this.method.returnsVoid()) { throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + this.command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + this.method.getReturnType() + ")."); } else { return result; } }‘仍然是通过SqlSession中API来db进行交互’
SqlCommand - sql语句对象 - 解析出来的sql语句就被封装到了SqlCommand
String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName; = this.command.getName(); sqlSession.api方法(namespace.id属性值,..)
输入参数类型
接口中的方法是单个参数,sql标签需要指定参数的类型 - parameterType - 支持类型的别名,如果是自定义的类型,需要提前在mybatis-config.xml主配置文件中进行配置的
散列的类型 - 一定要配置@Param注解 - 无需在sql标签中写parameterType
希望接口更加具备可拓展性的话 - 不建议使用散列的数据
如果哪天条件增多/减少,接口是需要变化的.接口是给外部调用的.
使用第三方实体类来封装条件
使用Map来封装条件
返回参数类型
- 单个参数 - resultType
- 查询出来的列,没有对应的实体类.需要创建第三方dto对象来封装查询结果
- 使用Map来作为返回类型
动态SQL语句
mybatis映射文件的灵魂 - 支持动态sql以及sql片段[封装sql,然后支持多次调用]
if标签
<select id="findIf" resultType="video">
select * from t_video where 1=1
<if test="title!=null">
and title like '%${title}%'
</if>
<if test="price!=null">
and price >= #{price}
</if>
</select>
where标签
- 作用 - 查询语句后面自动拼接where语句
- 作用 - 去除where语句后面的第一个条件前面的条件连接符号[and,or]
<select id="findIf" resultType="video">
select * from t_video
<where>
<if test="title!=null">
and title like '%${title}%'
</if>
<if test="price!=null">
and price >= #{price}
</if>
</where>
</select>
set标签
更新
- 生成set语句
- 去除最后一个更新列的最后一个逗号
<update id="update" parameterType="video">
update t_video
<set>
<if test="title!=null">
title=#{title},
</if>
<if test="price!=null">
price=#{price},
</if>
<if test="videoUrl!=null">
video_url=#{videoUrl}
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
foreach标签
动态 SQL 的另一个常见使用场景是对集合进行遍历(尤其是在构建 IN 条件语句的时候)
<select id="findIds" parameterType="list" resultType="video">
select * from t_video where id in
<foreach open="(" close=")" separator="," collection="ids" item="item">
#{item}
</foreach>
</select>
collection属性值可以为list集合的默认的键名 - list,当然自定list的键名,方法参数加上@Param("ids")
item代表是集合中的每一项元素
练习
/**
* 保存多条视频信息
* @param videos
* @return
*/
int saveList(List<Video> videos);
注解开发
t_comment 评论表
鼓励单表操作
注解开发和xml开发并存的
public interface CommentsMapper { @Select("select * from t_comment") List<Comments> findAll(); @Delete("delete from t_comment where id=#{id}") int delById(Integer id); @Insert("insert into t_comment values(#{id},#{userId},#{videoId},#{content},#{commentId})") int save(Comments comments); @Select("select * from t_comment where id=#{id}") Comments getById(Integer id); }
sql片段
主要的作用就是用来封装sql语句,以便sql语句的多次复用.
UserMapper.xml
- sql片段就在当前的映射文件中
<!-- 定义一个sql片段--> <sql id="findAllUserSql"> select * from t_user </sql> <!-- sql标签的id属性的值**一定要和mapper**接口中的方法的名称**高度保持一致--> <select id="findAll" resultType="user"> <!--select * from t_user--> <!--引用sql片段--> <include refid="findAllUserSql"></include> </select> <select id="getById" resultType="user" parameterType="int"> <include refid="findAllUserSql"></include> where id=#{value} </select>
需要在A文件中引入B文件中的sql片段
<include refid="B映射文件的namespace.sql片段id属性值">
resultMap - 继承性
应用场景一: 当查询的列值不能自动映射/绑定实体类的属性的时候,需要通过resultMap来进行一一绑定.
<resultMap id="getByIdMap" type="user"> <id column="uid" property="id"></id> <result column="uname" property="username"></result> </resultMap> <select id="getById" resultMap="getByIdMap" parameterType="int"> select id uid,username uname from t_user where id=#{id} </select>
这条语句只需要取出俩条数据 - 手动封装了俩条数据即可
!-- 定义一个sql片段--> <sql id="findAllUserSql"> select id uid,username uname,password,birthday from t_user </sql> <select id="findAll" resultMap="findAllMap"> <!--select * from t_user--> <!--引用sql片段--> <include refid="findAllUserSql"></include> </select> <resultMap id="findAllMap" type="user" extends="getByIdMap"> <result column="password" property="password"></result> <result column="birthday" property="birthday"></result> </resultMap>
需要把所有的列数据进行查询绑定- resultMap标签是允许被继承的.
日志的配置
Mybatis 通过使用内置的日志工厂提供日志功能。内置日志工厂将会把日志工作委托给下面的实现之一:
- SLF4J
- Apache Commons Logging
- Log4j 2
- Log4j - 配置方式比较简单 - 选用的
- JDK logging
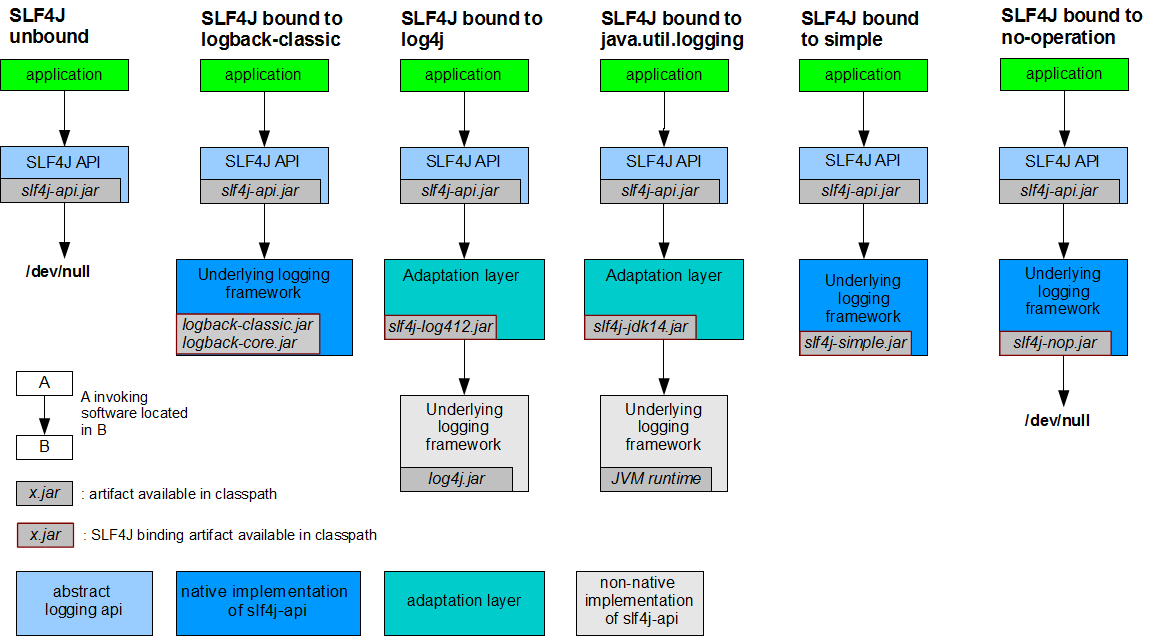
SLF4J日志框架
市面提供了SLF4J - 日志门面-接口
slf4j-api.jar - 日志接口 - slf4j-api-1.7.30.jar - 项目中仅仅只有日志的接口,而没有实现jar - 不ok
springboot框架中推荐使用的日志实现 - logback
- 必须先引入日志门面 - 日志接口 slf4j-api.jar
- 必须引入日志的具体的实现 - logback-core.java
不需要中间适配包的原因是slf4j日志框架的创造者和logback日志具体实现的创造者是同一个作者
mybatis中想要使用log4j
- ①引入日志接口slf4j-api.jar - pc的接口 B -> 5个方法
- ②slf4j-log412.jar - 适配包 - usb转接口 C extends B
- ③引入log4j.jar - log4j日志具体实现 - 网线接口 D extends C -> 10个方法
slf4j日志接口的作者和log4j作者不是同一个人
配置文件
#log4j.rootLogger=debug,stdout,logfile
# ERROR - 日志的级别,只有出现错误才会输出日志信息.
# stdout - 将日志信息输出到控制台,不会输出到日志文件
# logfile - 将日志信息输出到日志文件中去.不会在控制台输出
log4j.rootLogger=INFO,stdout
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.Target=System.err
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.SimpleLayout
log4j.appender.logfile=org.apache.log4j.FileAppender
# 日志文件的路径
log4j.appender.logfile.File=jbit.log
log4j.appender.logfile.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.logfile.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %F %p %m%n
# 项目中调用哪个接口中的方法的时候,才会产生日志信息.
log4j.logger.tech.aistar.mapper=DEBUG
#log4j.logger.com.mybatis.common.jdbc.SimpleDataSource=DEBUG
#log4j.logger.com.mybatis.common.jdbc.ScriptRunner=DEBUG
#log4j.logger.com.mybatis.sqlmap.engine.impl.SqlMapClientDelegate=DEBUG
#log4j.logger.java.sql.Connection=DEBUG
#log4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUG
#log4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG
#log4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=DEBUG
<!-- 开启小驼峰命名映射-->
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
<!-- 控制台显示sql语句-->
<setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/>
</settings>
日志的显示级别
log4j定义了8个级别的log(除去OFF和ALL,可以说分为6个级别),优先级从高到低依次为:OFF、FATAL、ERROR、WARN、INFO、DEBUG、TRACE、 ALL。
ALL 最低等级的,用于打开所有日志记录。
TRACE designates finer-grained informational events than the DEBUG.Since:1.2.12,很低的日志级别,一般不会使用。
DEBUG 指出细粒度信息事件对调试应用程序是非常有帮助的,主要用于开发过程中打印一些运行信息。
INFO 消息在粗粒度级别上突出强调应用程序的运行过程。打印一些你感兴趣的或者重要的信息,这个可以用于生产环境中输出程序运行的一些重要信息,但是不能滥用,避免打印过多的日志。
WARN 表明会出现潜在错误的情形,有些信息不是错误信息,但是也要给程序员的一些提示。
ERROR 指出虽然发生错误事件,但仍然不影响系统的继续运行。打印错误和异常信息,如果不想输出太多的日志,可以使用这个级别。
FATAL 指出每个严重的错误事件将会导致应用程序的退出。这个级别比较高了。重大错误,这种级别你可以直接停止程序了。
OFF 最高等级的,用于关闭所有日志记录。
从上到下 - 输出的日志信息肯定是越来越少的.
作业
用现有的知识完成下面两道查询
- 根据视频的id来查询视频信息,顺便加载出该视频的用户信息
- 根据用户的id来查询用户信息,顺便加载出该用户下所有的视频信息
- 作业提交地址 - http://xzc.cn/J2Q0qw2wnj
加载one的一方
无论是1加载1,还是多加载1
查询什么,存储到内存哪里[对象]? - 实体对象类型[有表对应]/dto对象
搓的方式
- dto散列的属性和查询列对上号 - resultType
- resultMap - dto直接关联对象即可.直接使用OGNL语法 - 单个对象.属性,不能用集合对象.属性
resultType - 查询出来的列 - pojo属性一致 - 实现自动绑定.
需要自定义一个对象,来封装这些查询列的结果
public class VideoUserVo { private Integer id; private String title; private Date createDate; private Double price; private String videoUrl; //表中的外键是什么,此处就写什么. private Integer userId; private String username; private String password; private Date birthday; }或者使用第三方实体类来进行一个关心的维护,而我们的mybatis支持ognl语言[对象导航语言] - 必须维护的是单个对象
使用resultMap<resultMap id="getVideoWithUser2Map" type="videoUserVo2"> <!-- 此处就是OGNL语法,可以将查询出来的结果映射到videoUserVo2管理的单个对象的video对象的id属性中去--> <!-- ognl - 反射 - video -> getVideo -> Method -> videoUserVo2->invoke -> Video对象--> <!-- -> Video-Class,id -> setId反射调用--> <!-- 手动封装video相关属性--> <id column="id" property="video.id"></id> <result column="title" property="video.title"></result> <result column="price" property="video.price"></result> <result column="create_date" property="video.createDate"></result> <result column="video_url" property="video.videoUrl"></result> <result column="user_id" property="video.userId"></result> <result column="user_id" property="user.id"></result> <result column="username" property="user.username"></result> <result column="password" property="user.password"></result> <result column="birthday" property="user.birthday"></result> </resultMap> <select id="getVideoWithUser2" resultMap="getVideoWithUser2Map" parameterType="int"> select tv.*,u.username,u.password,u.birthday from t_user u join t_video tv on u.id = tv.user_id where tv.id=21 </select>
association
专门用来映射一的一方
作用:用来把查询出来的结果绑定到type指定的类型中关联的那个单个对象某个属性上.
public class VideoUserVo2 implements Serializable { private Video video; private User user; }
<resultMap id="getVideoWithUser3Map" type="videoUserVo2"> <!-- 绑定一的一方--> <association property="video" javaType="video"> <id column="id" property="id"></id> <result column="title" property="title"></result> <result column="price" property="price"></result> <result column="create_date" property="createDate"></result> <result column="video_url" property="videoUrl"></result> <result column="user_id" property="userId"></result> </association> <association property="user" javaType="user"> <result column="user_id" property="id"></result> <result column="username" property="username"></result> <result column="password" property="password"></result> <result column="birthday" property="birthday"></result> </association> </resultMap> <select id="getVideoWithUser3" resultMap="getVideoWithUser3Map" parameterType="int"> select tv.*,u.username,u.password,u.birthday from t_user u join t_video tv on u.id = tv.user_id where tv.id=21 </select>
resultMap
单表的手动映射的结果进行一个单独的封装 - 查所有列
common-mapper.xml - 存放公共的resultMap
一定要在mybati-config.xml文件中进行读取
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="common"> <resultMap id="userIdMap" type="user"> <id column="id" property="id"></id> </resultMap> <resultMap id="userMap" type="user"> <result column="username" property="username"></result> <result column="password" property="password"></result> <result column="birthday" property="birthday"></result> </resultMap> <resultMap id="userAllMap" type="user" extends="userMap"> <id column="id" property="id"></id> </resultMap> <resultMap id="videoIdMap" type="video"> <id column="id" property="id"></id> </resultMap> <resultMap id="videoAllMap" type="video" extends="videoIdMap"> <result column="title" property="title"></result> <result column="price" property="price"></result> <result column="create_date" property="createDate"></result> <result column="video_url" property="videoUrl"></result> <result column="user_id" property="userId"></result> </resultMap> </mapper><resultMap id="getVideoWithUser4Map" type="videoUserVo2"> <!-- 绑定一的一方--> <association resultMap="common.videoAllMap" javaType="video" property="video"></association> <association property="user" javaType="user" resultMap="common.userMap"></association> </resultMap> <select id="getVideoWithUser4" resultMap="getVideoWithUser4Map" parameterType="int"> select tv.*,u.username,u.password,u.birthday from t_user u join t_video tv on u.id = tv.user_id where tv.id=21 </select>
延迟加载
懒加载
查询many方,希望延迟加载出one方.
分析 - select tv.*,u.username,u.password,u.birthday from t_user u join t_video tv on u.id = tv.user_id where tv.id=21
进行了多表的关联查询 - 不管实际的业务 - 俩张表中的数据全部加载出来了 - 迫切
延迟加载
- 只查询many方 - 视频
- 如果业务中需要加载出视频对应的one方法[User] - 才会去查询这个视频的用户信息.如果不需要one方,不会去执行查询user的sql.
第一种方式 - 推荐
回忆jdbc写法 - 对象只会id[Video类 - user_id属性]
IVideoDao.java - Video getById(Integer id);//根据id查询视频 select * from t_video where id=?
IUserDao.java - User getById(Integer id);//根据用户id查询用户 select * from t_user where id=?
按需加载 - 必须在业务层中进行一个处理了.
IVideoSerivce.java
Video findById(Integer id);
VideoVo findVideoUser(Integer id);
业务只需要加载视频信息 - videoDao.findById(1);
需要加载视频以及对应的user
@Override
public VideoVo findVideoUser(Integer id){
VideoVo vo = new VideoVo();
Video v = videoDao.findById(1);
User user = userDao.findById(v.getUserId());
vo.setVideo(v);
vo.setUser(user);
return vo;
}
第二种方式 - mybatis特性
resultMap + association/collection
需要开启一下延迟记载的设置 - mybatis-config.xml
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> <!-- 只要触发对象的equals,clone,hashCode,toString - 延迟效果都会失效了.--> <setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="clone"/>只要触发对象的equals,clone,hashCode,toString - 延迟效果都会失效了.
xml
<!-- 延迟加载--> <select id="getVideoLazyLoadUser" resultMap="videoLazyMap" parameterType="int"> select * from t_video where id=#{id} </select> <resultMap id="videoLazyMap" type="videoUserVo2"> <!-- 手动映射--> <association property="video" javaType="video"> <id column="id" property="id"></id> <result column="title" property="title"></result> <result column="price" property="price"></result> <result column="create_date" property="createDate"></result> <result column="video_url" property="videoUrl"></result> <result column="user_id" property="userId"></result> </association> <!-- 延迟加载出videoUserVo2 - user信息 column = "user_id" 把该列的值传给了select引用的查询语句中的#{id} --> <association property="user" column="user_id" select="tech.aistar.mapper.UserMapper.getById"></association> </resultMap>
加载many的一方
根据用户的id来查询用户信息,顺便加载出该用户下所有的视频信息
collection
public class UserQueryVo extends User {
private List<Video> videoList;
}
<select id="findUserWithVideos" resultMap="findUserWithVideosMap" parameterType="int">
select u.id uid,u.username,u.password,u.birthday,v.* from t_user u
left join t_video v on v.user_id = u.id where u.id=#{id};
</select>
<resultMap id="findUserWithVideosMap" type="userQueryVo">
<!-- 处理user对象的属性的绑定-->
<id column="uid" property="id"/>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<result column="password" property="password"/>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday"/>
<!-- 绑定到一个集合属性videoList ofType集合属性的泛型-->
<collection property="videoList" ofType="video">
<result column="id" property="id"></result>
<result column="title" property="title"/>
<result column="create_date" property="createDate"/>
<result column="price" property="price"/>
<result column="video_url" property="videoUrl"/>
<result column="user_id" property="userId"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
public class UserQueryVo implements Serializable {
private User user;
private List<Video> videoList;
}
mybatis逆向工程
由db设计来自动构成entity以及mapper接口以及mapper的映射文件
逆向工程的配置文件是config.xml文件中 - 关键的配置信息
<!-- 数据库连接信息 --> <jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/j03s?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC" userId="root" password="root"> </jdbcConnection><!-- targetProject:生成PO类的位置 --> <javaModelGenerator targetPackage="tech.aistar.entity" targetProject="src/"> <sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="tech.aistar.mapper" targetProject="src/"><!-- 指定数据库表 <domainObjectRenamingRule searchString="^T" replaceString=""></domainObjectRenamingRule> T一定是大小,表的前缀.t_user,t_video --> <table tableName="t_user"> <domainObjectRenamingRule searchString="^T" replaceString=""></domainObjectRenamingRule> </table> <table tableName="t_video"> <domainObjectRenamingRule searchString="^T" replaceString=""></domainObjectRenamingRule> </table>如果大家设计的表没有带前缀,直接写
<table tableName="user"></table>
启动startServer
Mybatis逆向工程生成的Example使用方式 - api方式来替代手写sql方式
@Test
public void testExample(){
//面向sql -> 面向对象编程
//List<User> selectByExample(UserExample example);
UserExample userExample = new UserExample();
//准则 - 条件
UserExample.Criteria criteria = userExample.createCriteria();
//admins - 精确查找
//criteria.andUsernameEqualTo("admins");
//模糊查询
// criteria.andUsernameLike("%yan%");
//username模糊查询,id>=5
criteria.andUsernameLike("%yan%").andIdGreaterThanOrEqualTo(5);
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectByExample(userExample);
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
@Test
public void testFindExample(){
UserExample userExample = new UserExample();
//username=yang2或者id=1
UserExample.Criteria c1 = userExample.createCriteria();
c1.andUsernameEqualTo("yang2");
//如果是or - 连接另外一个条件
UserExample.Criteria c2 = userExample.createCriteria();
c2.andIdEqualTo(1);
userExample.or(c2);
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectByExample(userExample);
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
分页查询
针对单表操作进行分页.针对的是实体对象进行分页的.
导入 - pagehelper-4.1.6.jar,jsqlparser-1.0.jar
分页的动作肯定是在service层进行的 - 将来的动作.
mybatis-config.xml
<plugins> <plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper"></plugin> </plugins>
如果数据量特别大 - 分页插件的效率就会变得很低 - 手写分页,改写分页插件.
limit性能是受到偏移量的影响,偏移量[第一个参数?]越大,性能越低
select id uid,username uname,password,birthday from t_user limit ?,?
作业
查询某个用户的发布的某个视频下的所有的评论以及回复信息 - 四表操作 - DTO对象如何设计
某个用户删除某条视频[级联删除这条视频下所有的评论和回复]
db表交上来 - 不要等我 - 点击去看功能
sql脚本 - 建表语句以及模拟insert语句
Mybatis缓存
一级缓存
mybatis中是自动开启一级缓存的.
SqlSession = Connection[Jdbc中的一次连接] + Cache[默认开启的就是一级缓存]
一级缓存是SqlSession级别的.
演示:
package tech.aistar.cache; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.junit.Test; import tech.aistar.dao.IUserDao; import tech.aistar.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl; import tech.aistar.mapper.UserMapper; import tech.aistar.model.entity.User; import tech.aistar.util.MybatisUtil; import java.sql.SQLException; /** * 本类用来演示: mybatis的一级缓存 * * @author: success * @date: 2021/9/6 8:34 上午 */ public class TestFirstLevelCache { @Test public void testOneCache(){ //1. 获取连接 SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSession(); UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); //第一次调用getById方法 - 日志 - sql记录 //出现一次sql记录 - 和db交互了一次 //如果能够顺利返回一条记录,如果db中不存在,则直接返回null //否则,将这条语句封装的那个实体对象放入到一级缓存中[内存中] User user = userMapper.getById(1); System.out.println(user); System.out.println("===演示一级缓存的效果==="); //再次查询相同id的用户 //观察控制台出现了几条sql记录 //效果:最终控制台仅仅只会出现一条sql语句 //说明了虽然调用了2次,但是只和db产生了一次交互 //为了减少程序和磁盘一个IO交互的次数 - 提高查询效率 //查询对象的步骤 //1. 优先到一级缓存中去查找是否有和这个实体对象 // 如果有,直接从一级缓存中将对象直接返回出来 //2. 如果一级缓存中木有.那么才会有db进行交互,控制台看到产生一条sql记录 User user2 = userMapper.getById(1); System.out.println(user2); //true System.out.println(user == user2); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { MybatisUtil.closeSession(sqlSession); } } }
一级缓存中什么场景下会失效?
sqlSession.close();//整个sqlSession整个空间都会被回收.
sqlSession.commit();//清空一级缓存.
查询的流程
- 优先到一级缓存中去查询是否存在这个实体对象.如果有直接返回.否则才会和db进行交互
- 目的好处 - 为了提高查询效率的.
二级缓存
mybatis并没有自动开启二级缓存,手动配置启动二级缓存
mybatis-config.xml
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>需要让哪个mapepr使用二级缓存,就需要在哪个mapper映射文件中添加
<mapper namespace="tech.aistar.mapper.UserMapper"> <!--启用二级缓存--> <cache/>二级缓存跨sqlSession级别,属于mapper级别的
剖析运行结果
@Test
public void testSecondCache(){
//1. 获取连接
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//①
User user = userMapper.getById(1);
System.out.println(user);
sqlSession.commit();//清空一级缓存
System.out.println("===演示二级缓存的效果===");
//②即使一级缓存被清空了,但是此处仍然是不会出现sql语句的.
//又会到二级缓存中去查找 - 很幸运 - 匹配到.
//Cache Hit Ratio [tech.aistar.mapper.UserMapper]: 0.5
User user2 = userMapper.getById(1);
System.out.println(user2);
//true
System.out.println(user == user2);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
MybatisUtil.closeSession(sqlSession);
}
}
控制台日志信息
//① User user = userMapper.getById(1);//优先到二级缓存中去查找,所以缓存命中[二级缓存]率为0.0
DEBUG - Cache Hit Ratio [tech.aistar.mapper.UserMapper]: 0.0
DEBUG - ==> Preparing: select * from t_user where id=?
DEBUG - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
DEBUG - <== Total: 1
User{id=1, username='admins', password='654321', birthday=Thu Aug 26 00:00:00 CST 2021}
===演示二级缓存的效果===
WARN - As you are using functionality that deserializes object streams, it is recommended to define the JEP-290 serial filter. Please refer to https://docs.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=javase15&id=GUID-8296D8E8-2B93-4B9A-856E-0A65AF9B8C66
DEBUG - Cache Hit Ratio [tech.aistar.mapper.UserMapper]: 0.5
User{id=1, username='admins', password='654321', birthday=Thu Aug 26 00:00:00 CST 2021}
false
Process finished with exit code 0
细节部分
① User user = userMapper.getById(1); 背后: 1. 优先从一级缓存中去查找是否存在id=1的user对象,如果不存在执行2,存在,直接返回了 2. 再到二级缓存中去查找是否存在id=1的user对象.如果不存在,则会和db进行交互 select * from t_user where id=? 3. 将user对象散列的属性数据放一份到二级缓存.将整个user实体对象[整体]放入到一级缓存中. ②User user2 = userMapper.getById(1);测试部分 - user===user2 - true
//① User user = userMapper.getById(1); System.out.println(user); //sqlSession.commit();//清空一级缓存 System.out.println("===演示二级缓存的效果==="); User user2 = userMapper.getById(1); System.out.println(user2); //true System.out.println(user == user2);测试部分 user == user2 - false
User user = userMapper.getById(1);//一,二缓存都有 System.out.println(user); sqlSession.commit();//清空一级缓存,只剩下二级缓存有 System.out.println("===演示二级缓存的效果==="); User user2 = userMapper.getById(1);//user2是二级缓存中 System.out.println(user2); //false //原因就是因为将user对象散列的属性数据放一份到二级缓存, 放 -> 1 admins 123456 //再次从二级缓存中将散列的数据封装到一个新的user对象中 System.out.println(user == user2);
useCache属性
在mapper文件中加上了
标签,针对的是这个mapper文件中所有的查询语句都开启了二级缓存. 二级缓存也是需要占内存.
更新比较频繁的数据,null值比较多的数据 - 不适合缓存.
<select id="getById" resultType="user" parameterType="int" useCache="false"> select * from t_user where id=#{id} </select>com.intellij.rt.junit.JUnitStarter -ideVersion5 -junit4 tech.aistar.cache.TestSecondLevelCache,testSecondCache DEBUG - ==> Preparing: select * from t_user where id=? DEBUG - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer) DEBUG - <== Total: 1 User{id=1, username='admins', password='654321', birthday=Thu Aug 26 00:00:00 CST 2021} ===演示二级缓存的效果=== DEBUG - ==> Preparing: select * from t_user where id=? DEBUG - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer) DEBUG - <== Total: 1
第三方缓存
Ehcache技术 - 把内存中的数据 - 缓存到磁盘文件里.
Redis
非关系型的键值对数据库 - 缓存数据库,可以进行持久化操作.
mysql - Redis - mysql和Redis数据同步问题[避免从缓存中获取到脏数据]