数据字典
用户表 - 自定义的表 - 存储用户的数据
系统表 - 数据字典 - 存储的是用户表的元信息.
用户表仅仅可能只是系统表中的一个字段存在着而已.
类似于java.lang.Class
,所有的类都是属于Class的对象 - 类是用来描述对象.我们是可以通过Class对象的API来获取类的信息. Class用来描述类的类.
demo
tbl_comment
use information_schema; show tables; 发现里面有一个系统表 - TABLE_CONSTRAINTS - 数据字典 - 保存的是所有的表的约束信息. desc table_constraints; +--------------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | CONSTRAINT_CATALOG | varchar(512) | NO | | | | | CONSTRAINT_SCHEMA | varchar(64) | NO | | | | | CONSTRAINT_NAME | varchar(64) | NO | | | | | TABLE_SCHEMA | varchar(64) | NO | | | | | TABLE_NAME | varchar(64) | NO | | | | | CONSTRAINT_TYPE | varchar(64) | NO | | | | +--------------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 6 rows in set (0.01 sec) table_name,constraint_name,constraint_type 表名 约束名称 约束类型 --1. 查什么 --2. 到哪里查 -- 查看tbl_comment表中以上三个字段 mysql> select table_name,constraint_name,constraint_type from table_constraints where table_name='tbl_comment'; +-------------+-------------------------+-----------------+ | table_name | constraint_name | constraint_type | +-------------+-------------------------+-----------------+ | tbl_comment | PRIMARY | PRIMARY KEY | | tbl_comment | tbl_comment_id_fk | FOREIGN KEY | | tbl_comment | tbl_comment_user_id_fk | FOREIGN KEY | | tbl_comment | tbl_comment_video_id_fk | FOREIGN KEY | +-------------+-------------------------+-----------------+ -- 查看tbl_comment表中的列的名称[COLUMN_NAME],列的数据类型[COLUMN_TYPE] mysql> select column_name,column_type from columns where table_name='tbl_comment'; +-------------+-------------+ | column_name | column_type | +-------------+-------------+ | id | int(7) | | user_id | int(7) | | video_id | int(7) | | content | varchar(50) | | comment_id | int(7) | +-------------+-------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
索引基础篇
简介:mysql中不同的存储引擎的索引的实现方式是不同的.
索引最大的好处就是会提高查询效率,但是索引也是占内存空间,索引也是需要进行维护[更新 - 消耗时间]的.并不是索引建立的越多越好.
**5.7及其以后默认的存储引擎就是innodb,**之前默认采用的是myisam
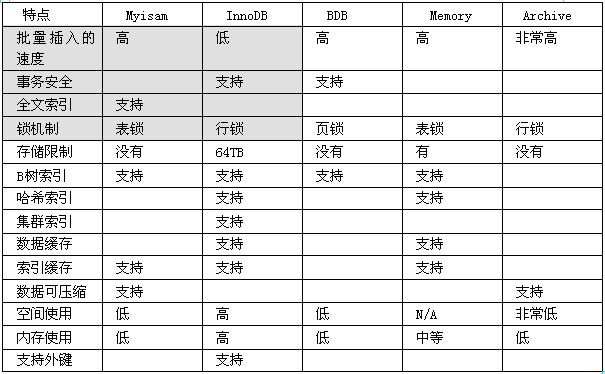
myisam和innodb有何区别
innodb支持事务,myisam不支持事务 [DTL命令是不支持的]
myisam支持全文索引.但是innodb不支持全文索引.
innode可以支持到行锁.myisam支持到表锁.
行锁的性能高于表锁.
innodb支持b+树索引 - 笔试索引的底层原理 = B+树相关
innodb支持外键约束的.
索引的底层 - 见高级篇
MyISAM
有单独的索引文件的,索引过多 - 索引文件变大(占空间的)
叶子节点中保存的是索引+物理行地址的
索引的本质:键值对(索引列值,物理行地址)
先判断查询是否走了索引,先查询索引文件,找到物理行地址
再由地址直接定位到数据表.
索引是单独的文件
InnoDB
- 索引文件不是一个单独的文件,它和数据文件是合二为一的.
- 索引和数据->数据文件中 -> 聚簇索引
索引算法
- B+Tree(索引数据结构)
- 聚簇索引 - mysql会自动选择主键列作为聚簇索引列
- 非叶节点 - 聚簇索引列的值
- 叶节点 - 聚簇索引列值以及真实的数据.
- 非聚簇索引
- 非叶节点 - 非聚簇索引列的值
- 叶节点 - 键值对(非聚簇索引列的值,主键值)
- 聚簇索引 - mysql会自动选择主键列作为聚簇索引列
优缺点
- 好处:加快了查询速度(select )
- 坏处:降低了增,删,改的速度(update/delete/insert),增大了表的文件大小(索引文件甚至可能比数据文件还大)
索引类型
普通索引(index):仅仅是加快了查询速度
给非唯一,非主键的列添加的索引.比如表中的某列字段经常被用来搜索,比如email create index 索引名 on 表名(列名); -- 删除 alter table 表名 drop index 索引名;唯一索引(unique):行上的值不能重复
如果创建列的时候,给该列添加了唯一约束unique.那么这个列默认就是唯一索引.主键索引(primary key):不能重复
如果某列是主键列,那么该列默认就是索引列. -- 删除主键索引.索引索引自动创建的.索引名是系统自动分配的,特殊的名称PRIMARY alter table 表名 drop primary key; -- show index from 表名; -- 查看数据字典 - 保存了所有表的索引信息.全文索引(fulltext):仅可用于 MyISAM 表,针对较大的数据,生成全文索引很耗时空间。
组合索引[覆盖索引]:为了更多的提高mysql效率可建立组合索引,遵循”最左前缀“原则。
俩列作为一个整体 - 实际上是构成了一个索引. where province = ? and city = ? create index pro_city_index on xx(province,city);
索引语法
创建索引总览
CREATE TABLE table_name(
[col_name data type]
[unique|fulltext][index|key] [index_name](col_name[length]) [asc|desc]
)
- unique|fulltext为可选参数,分别表示唯一索引、全文索引
- index和key为同义词,两者作用相同,用来指定创建索引
- col_name为需要创建索引的字段列,该列必须从数据表中该定义的多个列中选择
- index_name指定索引的名称,为可选参数,如果不指定,默认col_name为索引值
- length为可选参数,表示索引的长度,只有字符串类型的字段才能指定索引长度
- asc或desc指定升序或降序的索引值存储
索引使用方式
查看某张表上的所有索引
show index from tableName [\G,如果是在cmd窗口,可以换行];
建立索引
CREATE INDEX 索引名 ON 表名(列值)
删除索引 - alter table 表名 drop index 索引名;
drop table index_test; create table index_test( id int(7) primary key, a int(7), b int(7), c varchar(20), d varchar(20) ); insert into index_test values(1,100,10,'aaa','A'); insert into index_test values(2,300,30,'aba','BB'); insert into index_test values(3,200,20,'caa','CC'); insert into index_test values(4,100,10,'daa','DD'); insert into index_test values(5,500,50,'aad','FF'); -- 默认主键列就是属于索引列 - 主键索引 mysql> show index from index_test \G; *************************** 1. row *************************** Table: index_test Non_unique: 0 Key_name: PRIMARY Seq_in_index: 1 Column_name: id Collation: A Cardinality: 5 Sub_part: NULL Packed: NULL Null: Index_type: BTREE Comment: Index_comment: 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -- 给a列单独创建一个索引 - 普通索引 - 非聚簇索引 create index index_test_a on index_test(a); -- 删除普通索引 alter table index_test drop index index_test_a; -- 创建一个组合索引 - 非聚簇索引 -- 非聚簇索引 - 非主键列索引 -- 聚簇索引 - 主键列索引 -- a,b当成一个整体来处理 - 实际上仍然是只有一个索引 create index index_test_a_b on index_test(a,b); -- 给定一个索引的长度key_len,列的数据类型应该是字符串类型 create index index_test on index_test(c(1)); 比如c列是学生的名称 王三 王静静 王老二 王八犊子 王静二 王静三 -- 给某列创建索引的目的就是为了提高根据该列进行查询的效率 -- 索引长度是1,区分度不够.假设的是姓王的比较多. -- 并没有提高多少查询效率 -- 目录页 -> 王 -> 2页到10页 select * from student where c='王静%'; -- 长度为2 -- 目录页 -- 王三 - 2页 -- 王静 - 4页~5页 -- 王老,王八.... -- create index index_test on index_test(c(2)); -- 前俩个 select * from student where c='王静%'; -- 如果很多位重复,如何处理..... -- 自己了解...alter table 表名 add primary key(列名) –不要加索引名,因为主键只有一个
删除非主键索引
alter table 表名 drop index 索引名;
mysql>删除主键索引:
alter table 表名 drop primary key;
查看查询是否使用到了索引
mysql>explain select语句;
组合索引
(5)复合索引
create index 索引名 on 表(列1,列2,列n);
索引失效情况
面试题 - 数据库如何进行优化 - 谈到如何解决索引失效.
索引type从优到差:System–>**const–>eq_ref–>ref–>ref_or_null–>index_merge–>unique_subquery–>index_subquery–>**range–>index–>all(全表扫描的意思)
drop table index_test;
create table index_test(
id int(7) primary key,
a int(7),
b int(7),
c varchar(20),
d varchar(20)
);
insert into index_test values(1,100,10,'aaa','A');
insert into index_test values(2,300,30,'aba','BB');
insert into index_test values(3,200,20,'caa','CC');
insert into index_test values(4,100,10,'daa','DD');
insert into index_test values(5,500,50,'aad','FF');
-- 复合索引
create index index_test_abc on index_test(a,b,c);
-- 测试explain - 测试查询是否使用到了索引.
-- 测试主键索引
mysql> explain select * from index_test where id = 4;
+----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | index_test | NULL | const | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
主要就是观察type='const';
所谓创建索引 - 索引高级篇.
索引文件采取一个数据结构[b+树]用来专门存放索引.
为何根据索引查找比较快 - 先查索引[先查目录] - 进行定位到行的操作 - myisam中.
myisam中索引文件和数据文件.独立存储的,也是分开的存储.
1. 数据文件[磁盘上的]也就是所谓的表文件.加载到mysql内存中[select].
表里面的每一行在内存中也有一个内存地址.
2. 索引文件存储的是索引列的值以及该索引列对应的行记录的内存地址.
索引列 内存地址
1 0x7a
2 0x7b
3 0x7c
4 0x7d
5 0x7e
myisam索引 - 键值对索引[键 - 索引列值,值 - 行记录的内存地址]
键值对存储在B+树中.
select * from index_test where id = 4;
1. 根据id=4先到索引文件中去查找了[消耗时间的]
2. 找到id=4对应的行记录地址[唯一的映射关系]
3. 直接根据行记录地址定位到具体的一行,不需要在数据文件中进行一个全表扫描了.
-- 测试非索引列的查询 d
mysql> explain select * from index_test where d = 'DD';
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | index_test | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 5 | 20.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
Type='all' , 全表扫描 , 没有用到索引或者索引失效 , 从表里面的第一行一直扫描到最后一行 - 查询性能肯定是低下的.
遵循最左原则
简介:针对的是复合索引 - 查询语句where最左边的列一定要和创建复合索引的第一个列保持一致.
- 复合索引(a,b,c) - 必须要连续.
-- 创建复合索引的第一个列a
create index index_test_abc on index_test(a,b,c);
-- a,b,c都是生效的-100 | 10 | daa
explain select * from index_test where a=100 and b=10 and c='daa';
-- key_len 是73,三个索引都走了.
-- 比如b失效的场景,c也是失效
explain select * from index_test where b=10;//不走索引
explain select * from index_test where c='daa';//不走索引
-- 不生效 - mysql5.7以后对where语句进行了优化.
-- oracle中where语句如果跟了多个条件,执行顺序 - 从右到左
-- mysql中where语句条件默认是从左到右的.
-- mysql低版本中where c='daa' and a=100;//不会走索引的
-- mysql5.7优化,优化成where a=100 and c='add';//才会走索引.
-- a走了索引,c没有索引 - 特殊的场景 - 底层优化了.
explain select * from index_test where c='daa' and a=100;
-- key_len = 5
-- a列索引生效
explain select * from index_test where a = 100;
-- key_len = 5
-- a,b生效
explain select * from index_test where a=100 and b=10;
-- key_len = 10
-- 如果仅仅是根据a列查询,key_len是5,但是此时key_len是10.说明a,b索引都生效.
-- a列是走了索引,但是c列没有走索引
-- 必须要连续.这个是时候a和c是不连续的,中间跳过了b.所以只有a是生效的,但是c是不生效的.
explain select * from index_test where a=100 and c='daa';
-- key_len=5
范围之后索引列也会失效
-- a列和b列是走了索引的,但是c列没有走索引.因为c列是范围之后的判断
mysql>explain select * from index_test where a=100 and b>10 and c='daa';
-- 如果三个索引都生效 - key_len=73
-- 如果只有a,b走索引 - key_len=10 √
模糊查询
like '%'出现在末尾,仍然a,b,c都是走索引
-- key_len = 73 - a,b,c都是走了索引的
mysql> explain select * from index_test where a=100 and b=10 and c like 'd%';
-- like '%'如果出现在开始,不走索引的
-- 只有a,b是走了索引的,c是没有走索引的
-- key_len = 10
mysql>explain select * from index_test where a=100 and b=10 and c like'%d';
-- 只有a,b是走了索引的,c是没有走索引的
-- key_len=10
mysql>explain select * from index_test where a=100 and b=10 and c like'%d%';
索引列使用函数
索引列套在函数中使用,将会导致索引失效
-- 进行了ALL全表扫描
mysql> explain select * from index_test where abs(id)=1;
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | index_test | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 5 | 100.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
索引列参加了计算
-- 导致索引列失效
mysql> explain select * from index_test where id+1=2;
mysql> explain select * from index_test where id = 2 - 1;
索引列参加运算符
-- 给员工表的提成率列添加一个索引-普通索引
create index s_emp_cp on s_emp(commission_pct);
-- is null(没有走索引)和is not null(走索引)
-- is null - type='ALL'
mysql>explain select first_name,commission_pct from s_emp where commission_pct is null;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s_emp | NULL | ALL | s_emp_cp | NULL | NULL | NULL | 25 | 80.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
-- is not null type='range' - 走了索引的.
mysql> explain select first_name,commission_pct from s_emp where commission_pct is not null;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s_emp | NULL | range | s_emp_cp | s_emp_cp | 5 | NULL | 5 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
-- in(走索引 - range) not in(不走索引 - ALL)
mysql> explain select * from index_test where id in(1,2,3);
mysql> explain select * from index_test where id not in(1,2,3);
-- 能用关联解决的,尽量不要使用not
-- 找出没有选择任何一门课程的学生的信息
利用索引列查询出来的数据超过整张表的30%.
当数据量达到百万级别.
索引对应的重复的数据太多也是不适合创建索引的.
city=’苏州’
建立索引的策略
a. 索引不是越多越好的
因为索引也是需要占内容,也是需要到索引文件中去匹配索引的 - 需要消耗时间的.
更新数据的同时,我们更新索引数据.
- 主键列和唯一性列 √
- 不经常发生改变的[在update列数据的数据的时候,也会更新索引文件] √
- 满足以上2个条件,经常作为查询条件的列 √
- 重复值太多的列 ×
- null值太多的列 ×
查询效率
- 数据库读写分离.
- 分表分库 - 水平分割和垂直分割
- 使用专门的搜索引擎 - es - elasticsearch/solr
- 避免使用索引查询导致索引失效 - 规避问题.



